
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- COVID-19
- Association of Metabolic Syndrome with COVID-19 in the Republic of Korea
- Woo-Hwi Jeon, Jeong-Yeon Seon, So-Youn Park, In-Hwan Oh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):427-438. Published online November 26, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0105
- 4,431 View
- 242 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is reportedly a crucial risk factor for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Since the epidemiological studies that examine this association are few and include small samples, we investigated the relationship between MetS and COVID-19 severity and death using a larger sample in the Republic of Korea.
Methods
We analyzed 66,321 patients, 4,066 of whom had COVID-19. We used chi-square tests to examine patients’ characteristics. We performed logistic regression analysis to analyze differences in COVID-19 infection and clinical outcomes according to the presence of MetS.
Results
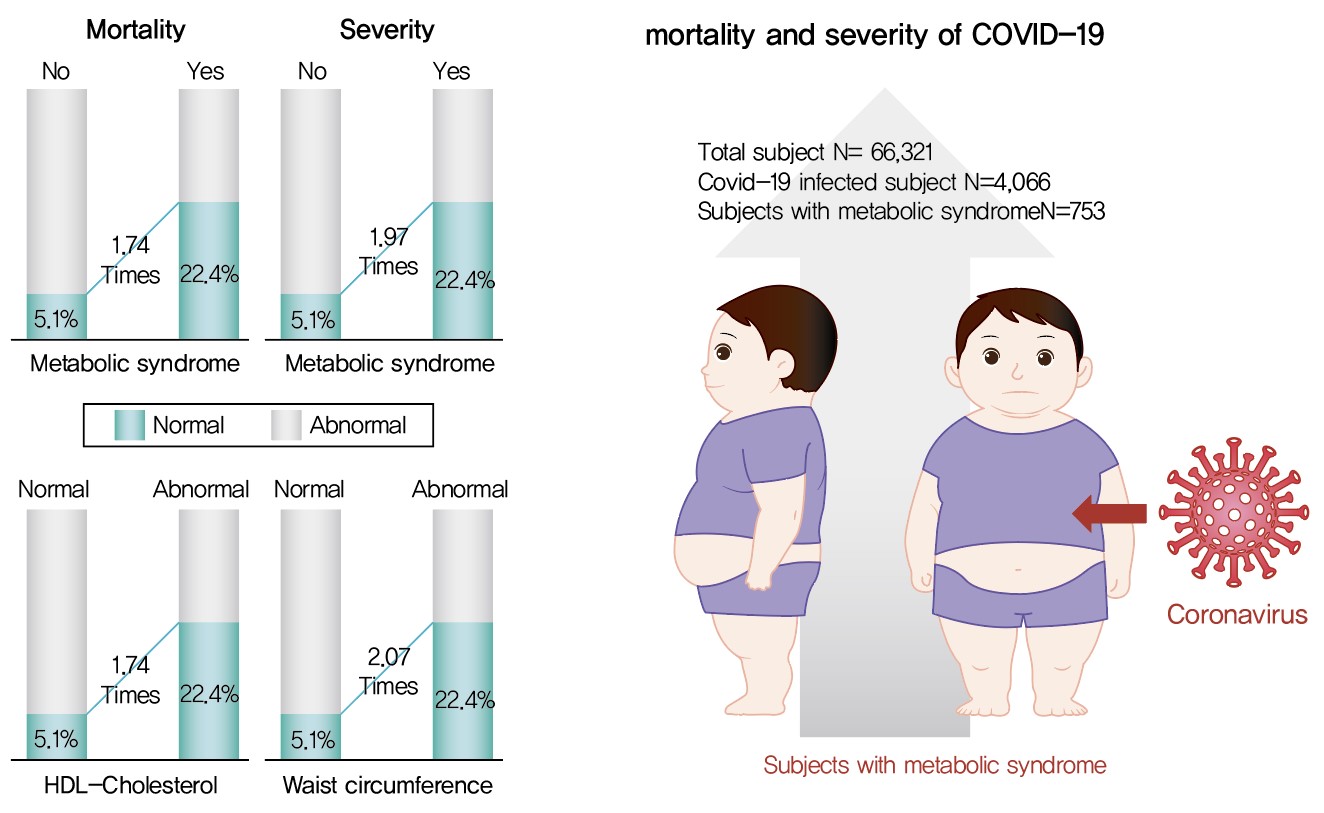
Although MetS was not significantly associated with COVID-19 risk, acquiring MetS was significantly associated with the risk of severe COVID-19 outcomes (odds ratio [OR], 1.97; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.34 to 2.91; P=0.001). The mortality risk was significantly higher in COVID-19 patients with MetS (OR, 1.74; 95% CI, 1.17 to 2.59; P=0.006). Patients with abnormal waist circumference were approximately 2.07 times more likely to develop severe COVID-19 (P<0.001), and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels were significantly associated with COVID-19; the mortality risk due to COVID-19 was 1.74 times higher in men with an HDL-C level of <40 mg/dL and in women with an HDL-C level of <50 mg/dL (P=0.012).
Conclusion
COVID-19 is likely associated with severity and death in patients with MetS or in patients with MetS risk factors. Therefore, patients with MetS or those with abnormal waist circumference and HDL-C levels need to be treated with caution. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Heterogeneity in familial clustering of metabolic syndrome components in the multiethnic GENNID study
Jia Y. Wan, Deborah Goodman, Sukh Makhnoon, Trina M. Norden‐Krichmar, Baolin Wu, Karen L. Edwards
Obesity.2024; 32(1): 176. CrossRef - Associated Factors with Changes of Metabolic Abnormalities among General Population in COVID-19 Pandemic
Eunjoo Kwon, Eun-Hee Nah, Suyoung Kim, Seon Cho, Hyeran Park
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2023; 23(2): 55. CrossRef - Association between metabolic syndrome and mortality in patients with COVID-19: A nationwide cohort study
Hyo Jin Park, Jin-Hyung Jung, Kyungdo Han, Jean Shin, Yoojeong Lee, Yujin Chang, Kyeyeung Park, Yoon Jeong Cho, Youn Seon Choi, Seon Mee Kim, Ga Eun Nam
Obesity Research & Clinical Practice.2022; 16(6): 484. CrossRef
- Heterogeneity in familial clustering of metabolic syndrome components in the multiethnic GENNID study

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





